
by web3fits | Feb 27, 2023 | Advanced, Web3Fits
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Ethereum, one of the world’s most popular cryptocurrencies and blockchain platforms. We’ll cover its history, how it works, its use cases, and how it has the potential to revolutionize a range of industries. What is Ethereum? Ethereum is a blockchain platform created in 2015 by programmer Vitalik Buterin. Like Bitcoin, it is a decentralized system that allows for the creation of digital currencies, but it goes beyond that, enabling developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Ethereum, like Bitcoin, is based on blockchain technology, which means that it is a secure and transparent system that is maintained by a large network of computers from around the world. 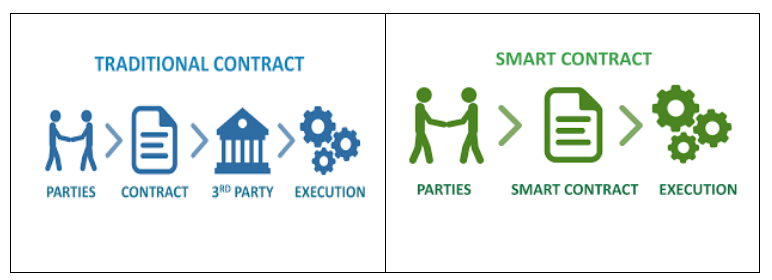
History of Ethereum
Ethereum was born out of a desire to create a more versatile blockchain system. At the time of Ethereum’s creation, Bitcoin was the only other existing blockchain. Bitcoin’s blockchain only had one use case at the time: to exchange digital currency. In 2013, at 19 years old, Vitalik Buterin, published a white paper outlining the concept of Ethereum. The platform was launched in 2015, and since then, it has become one of the most widely used blockchain systems in the world, with a market capitalization of over $200 billion at the time of writing.
How Ethereum Works
Prior to 2022, Ethereum ran on a proof-of-work system, which means that users could earn rewards by contributing computing power to the network. This is also known as mining. In September of 2022, Ethereum transitioned to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism used to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. Instead of relying on computational power, it uses a system where users “stake” their own cryptocurrency to verify transactions and earn rewards. By eliminating the need for computing power, Ethereum has been able to minimize its carbon footprint on the environment as well as position itself to further scale its blockchain to all corners of the globe. The platform uses its own cryptocurrency, called Ether, to facilitate transactions and smart contracts. Much like traditional contracts, Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. The decentralized nature of Ethereum means that it is resistant to censorship and interference by a controlling power, making it a popular choice for developers who want to create transparent, secure, and decentralized applications.
Use Cases for Ethereum
Ethereum has a wide range of potential use cases. Its most obvious use case is in the creation of digital currencies and the exchange of value. However, it has the potential to be much more than that. Ethereum can be used to create decentralized applications in fields such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. One big problem in modern-day supply chains is that it can be hard to know where things come from and where they’re going. This can lead to all sorts of problems, like environmental damage and labor abuses. With Ethereum, people can create special computer programs that track goods in a supply chain and make sure that everything is being done ethically and sustainably. Another big problem in modern-day finance is that big banks and financial institutions often control everything, which can lead to problems like high fees and unfair treatment. With Ethereum, people can create programs that allow people to send, receive, and trade digital money without needing a big bank or financial institution. This can help make finance more fair and accessible for everyone. Furthermore, Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities can be used to automate complex business processes, and its transparency and security make it an ideal platform for applications that require trust and accountability.
Revolutionizing Industries
Ethereum has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries. For example, in the finance industry, it can be used to create decentralized financial products, such as insurance policies and loans, without the need for intermediaries like banks. In healthcare, it can be used to create transparent and secure systems for storing patient data. And in supply chain management, it can be used to create transparent systems for tracking products from the manufacturer to the consumer. Ethereum is a powerful blockchain platform with the potential to revolutionize a range of industries. Its transparency, security, and versatility make it ideal for developers who want to create decentralized applications and smart contracts. As more and more businesses and organizations adopt Ethereum, we are likely to see it transform how we interact with technology, money, and each other.

by web3fits | Feb 22, 2023 | Intermediate, Web3Fits
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the way we think about money and value transfer. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, introduced the world to the idea of decentralized digital currencies. Today, there are thousands of different cryptocurrencies, each with its unique use cases and applications. In this article, we will explore ten different categories of cryptocurrencies and their respective use cases.
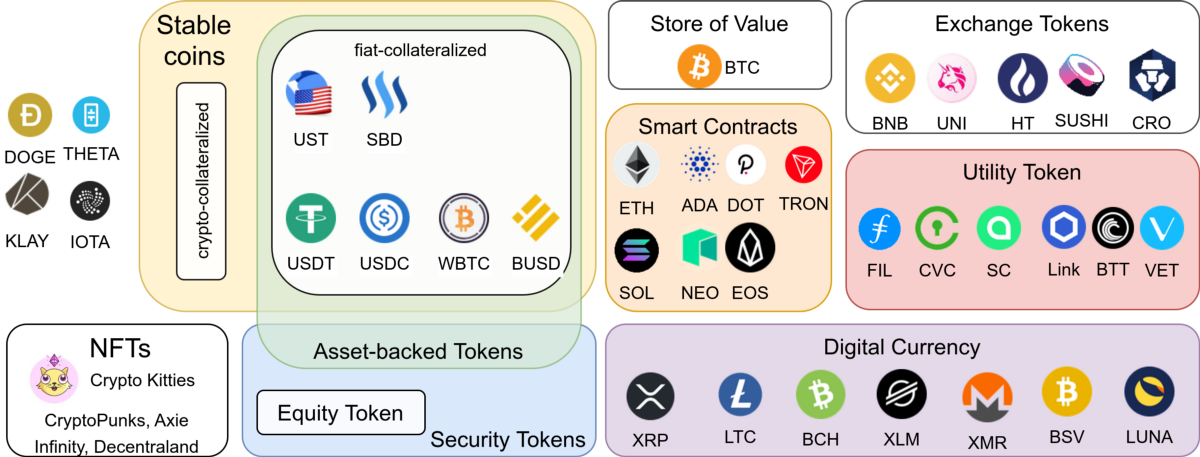
1. Currency Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that function as a medium of exchange, just like traditional currencies. The most well-known currency in cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, but there are many others like Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Ripple. The primary use case for currency cryptocurrencies is to enable fast, secure, and cheap payments without the need for intermediaries like banks.
2. Privacy Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that prioritize user privacy and anonymity. Privacy cryptocurrencies utilize advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure transactions are anonymous and cannot be traced back to their users. Examples of popular privacy cryptocurrencies include Monero, Zcash, and Dash. The primary use case for privacy cryptocurrencies is to enable users to transact without being tracked or surveilled.
3. DeFi Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. DeFi refers to a new financial system built on top of blockchain technology, enabling people to borrow, lend, and trade without the need for traditional financial intermediaries such as banks. Popular DeFi cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Chainlink, and Uniswap. The primary use case for DeFi cryptocurrencies is to enable the creation of a decentralized financial system that is open, transparent, and accessible to everyone.
4. Stablecoins – These are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to stable assets like fiat currencies or commodities. They are designed to provide the stability of fiat currencies while still benefiting from the advantages of cryptocurrencies, such as fast and low-cost payments. Some popular stablecoins include Tether, USD Coin, and Dai. The primary use case for stablecoins is to provide a stable store of value and medium of exchange for the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
5. Governance Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies used to govern blockchain networks and make decisions about their direction and development. Examples of governance cryptocurrencies include Maker, Tezos, and Polkadot. The primary use case for governance cryptocurrencies is to enable a decentralized decision-making process that is more democratic and transparent than traditional centralized decision-making structures.
6. Cross-Chain Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that can be used to transfer value between different blockchain networks. These cryptocurrencies enable users to move value from one blockchain to another without the need for intermediaries. Examples of popular cross-chain cryptocurrencies include Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink. The primary use case for cross-chain cryptocurrencies is to enable interoperability between different blockchain networks and facilitate value transfer between them.
7. Energy Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies used to incentivize and reward the production and consumption of green energy. Energy cryptocurrencies like Solarcoin and Power Ledger use blockchain technology to track energy production and consumption, incentivizing users to produce and consume renewable energy. The primary use case for energy cryptocurrencies is to create an incentive system for the production and consumption of green energy.
8. Asset-Backed Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that are backed by real-world assets such as gold, real estate, or art. The value of these cryptocurrencies is tied to the value of the underlying asset. Examples of asset-backed cryptocurrencies include Paxos Gold and Tether Gold. The primary use case for asset-backed cryptocurrencies is to provide a stable store of value that is pegged to a physical asset.
9. Identity Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that are used to establish and verify identities in a decentralized manner. Identity cryptocurrencies like Civic and SelfKey enable users to create and manage their own digital identities, giving them control over their personal information and protecting them from identity theft. The primary use case for identity cryptocurrencies is to create a decentralized and secure system for managing identity.
10. Gaming Cryptocurrencies – These are cryptocurrencies that are designed for use in video games and other online gaming applications. Gaming cryptocurrencies like Enjin and Decentraland enable players to buy, sell, and trade virtual assets within games. The primary use case for gaming cryptocurrencies is to provide a secure and transparent system for buying and selling in-game assets.
The world of cryptocurrencies is vast and varied, with new use cases and applications emerging all the time. The ten categories of cryptocurrencies we’ve explored in this article represent just a small slice of what is possible with blockchain technology. As cryptocurrencies continue to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases and applications emerge.

by web3fits | Feb 9, 2023 | Beginner, Web3Fits
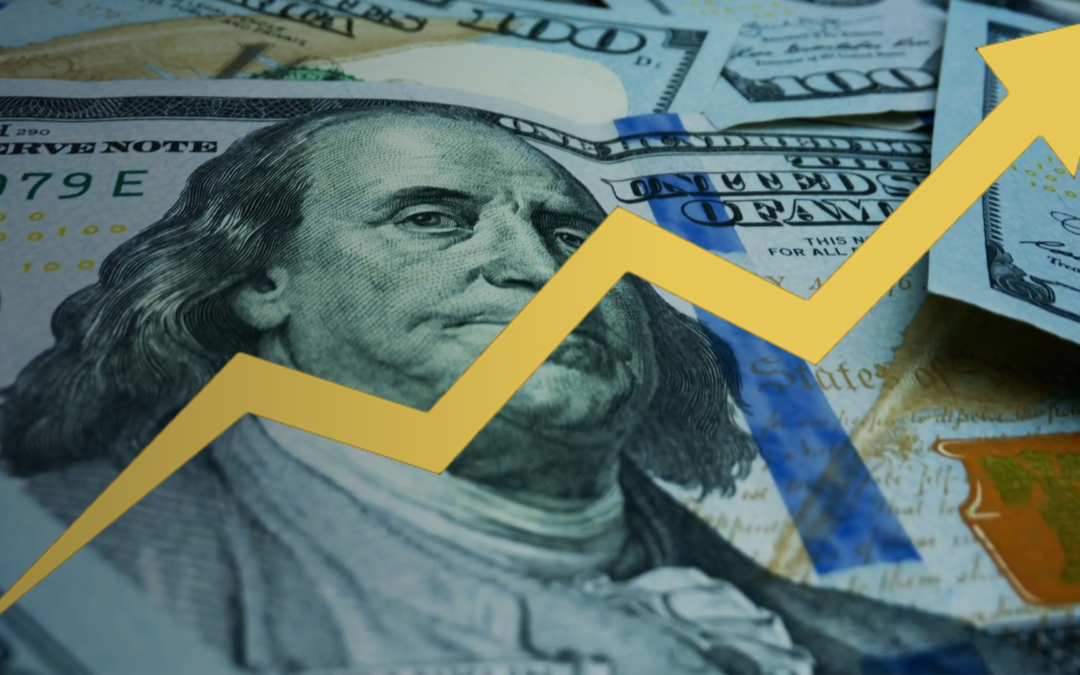
The history of failed money is a fascinating topic that can teach us important lessons about the value of the currency and the role of government in maintaining a stable economy. Throughout history, there have been countless examples of currencies that have lost value, leading to economic collapses and widespread suffering. Some of the most notable examples include the Roman Empire, Venezuela, Zimbabwe, Ukraine, and Germany.
The root of all these collapses is a lack of faith in the government. When people lose confidence in their government’s ability to maintain a stable economy, they start to hoard currency, causing demand to drop and value to decline. In many cases, this lack of confidence stems from economic mismanagement, corruption, or other factors that undermine the government’s ability to maintain stability.
One of the key causes of currency collapses is inflation. Inflation occurs when the supply of money exceeds demand, leading to an increase in prices. This can happen for a number of reasons, including an increase in the supply of money through printing, a decrease in demand due to hoarding, or a decline in the value of the underlying assets that support the currency. When inflation gets out of control, it can lead to hyperinflation, where prices increase so rapidly that the currency becomes essentially worthless.
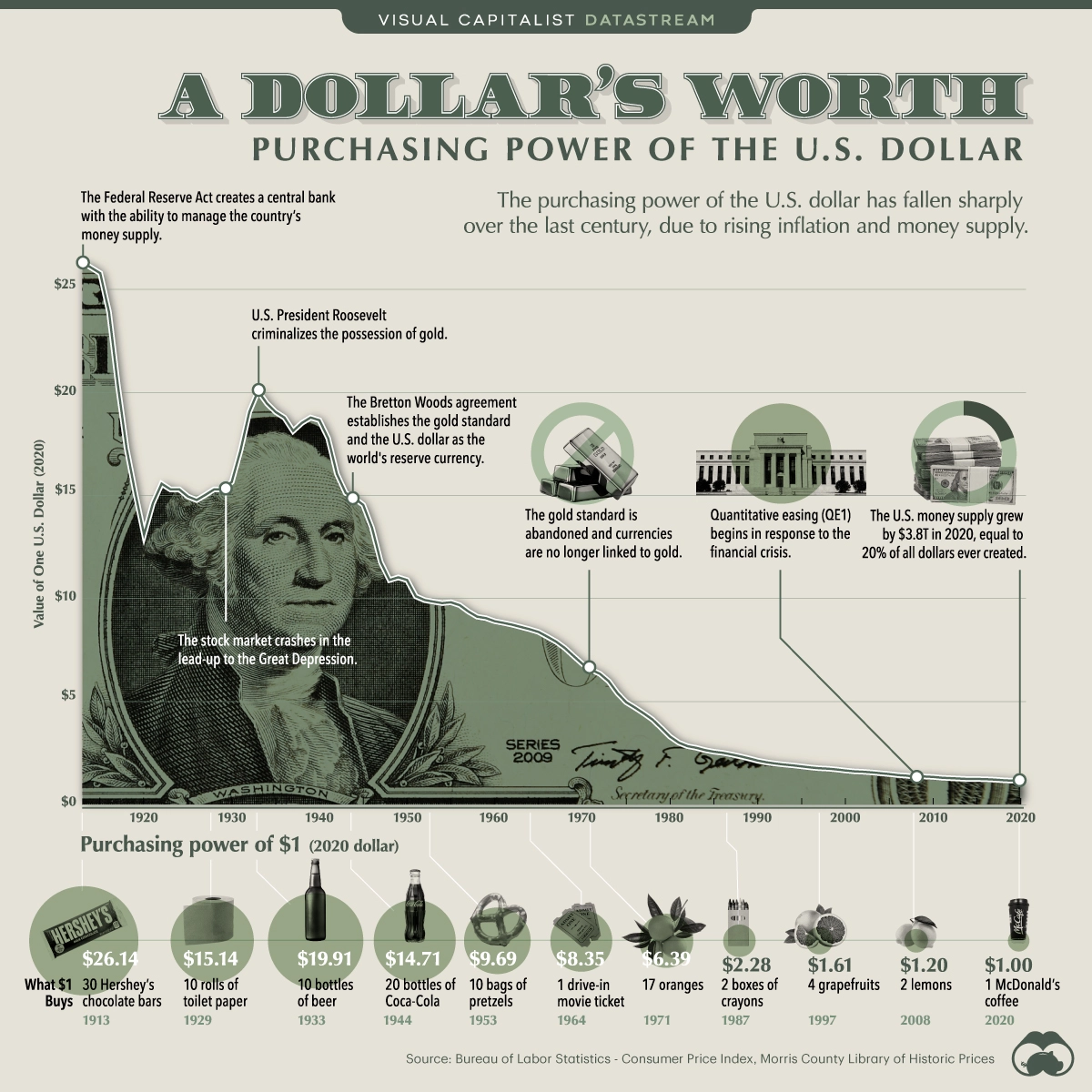
When the government prints more dollars, it adds to the system’s total amount. With more dollars in the system, the value of each dollar decreases. This happened many times in our history, hence why $1 now used to be the value of $26 in 1910.
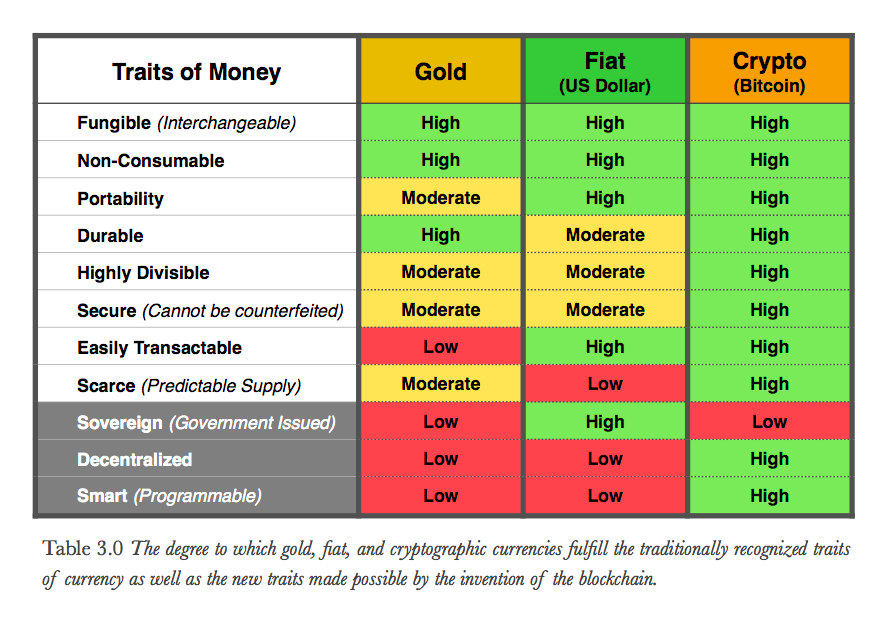
Cryptocurrency is being viewed as a solution to the problems of inflation and lack of trust in governments. Unlike traditional currencies, which are subject to central control and can be subject to inflationary pressures, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are decentralized and have a limited supply, making them less susceptible to the same issues. Cryptocurrencies use complex algorithms to control their supply, ensuring that inflation remains under control and the currency’s value remains stable.
The creation of cryptocurrency was directly influenced by a lack of faith in government and traditional financial institutions. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the fragility of the global financial system and led to widespread mistrust of banks and governments. This lack of trust led to the creation of Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, as a response to the problems of the traditional financial system. By using cryptography to secure transactions and decentralized networks to record transactions, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer a new way of storing and transferring value that is less susceptible to the issues of inflation and lack of trust that have plagued traditional currencies and financial institutions.
Currency collapses are often the result of a lack of trust in governments and the subsequent inflation that occurs. Cryptocurrency offers a solution to these issues, with its decentralized structure and fixed supply, making it less prone to inflation. The creation of cryptocurrency was a response to the declining trust in traditional financial institutions. By providing a secure, decentralized, and inflation-resistant option for storing and transferring value, cryptocurrency offers a new possibility in the world of finance.

by web3fits | Feb 6, 2023 | Advanced, Web3Fits
Bitcoin is a digital currency that has taken the world by storm. It’s a decentralized form of currency that allows people to make transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Behind the scenes, the process of Bitcoin Mining plays a crucial role in keeping the network secure and functioning properly. In this blog, we will explain what Bitcoin Mining is, how it works, the Bitcoin Halving, why it’s important, and the concept of Proof of Work.
Why is it Called Mining?
Bitcoin mining is called “mining” because it is similar to the process of mining for precious metals or minerals. Just like miners dig deep into the earth to extract gold or other valuable resources, Bitcoin miners use their computer power to “dig” into complex mathematical problems and extract Bitcoins as a reward. The term “mining” was chosen because it accurately describes the process of using computational power to solve problems and extract a reward. It also alludes to the finite nature of the resource, as there is a limited amount of bitcoins that can be mined, just like there is a limited amount of precious minerals that can be extracted from the earth.
Proof of Work
Proof of Work is the process of solving mathematical problems (mining) in order to add a block to the blockchain is called “Proof of Work”. It is a way of ensuring that the blocks are added to the chain in a secure and fair way. Miners have to put in a lot of effort and computing power in order to solve the problems and add the next block to the blockchain.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin Mining is a process where people use computers to solve complex mathematical problems and in return, they get brand new Bitcoins as a reward. Now I know what you thinking, “but Web3Fits, I’m terrible at math!!!”… but don’t worry. The computer handles all the problem-solving while you sit back and enjoy a nice cup of coffee. The process of solving these problems helps to keep the Bitcoin network secure and running smoothly. It is important to note that mining is not the only way to acquire Bitcoins. The process of mining is how brand-new Bitcoins enter the ecosystem. Bitcoins that have already been previously mined can be purchased OTC (over the counter from others Bitcoin holders) or through a cryptocurrency exchange.
How Does Mining Work?
When a problem is solved by a miner, it is called a “block”. Each block contains a list of all the transactions that have taken place on the Bitcoin network since the last block was mined. Miners compete with each other to be the first one to solve the problem and add the next block to the chain. Once a block is added, it cannot be changed, which helps to keep the transaction history secure.
Why is Mining Important?
Mining is important because it helps to keep the Bitcoin network secure and running smoothly. Miners are responsible for adding new blocks to the chain and verifying the transactions that take place on the network. Without mining, the Bitcoin network would not be able to function properly.
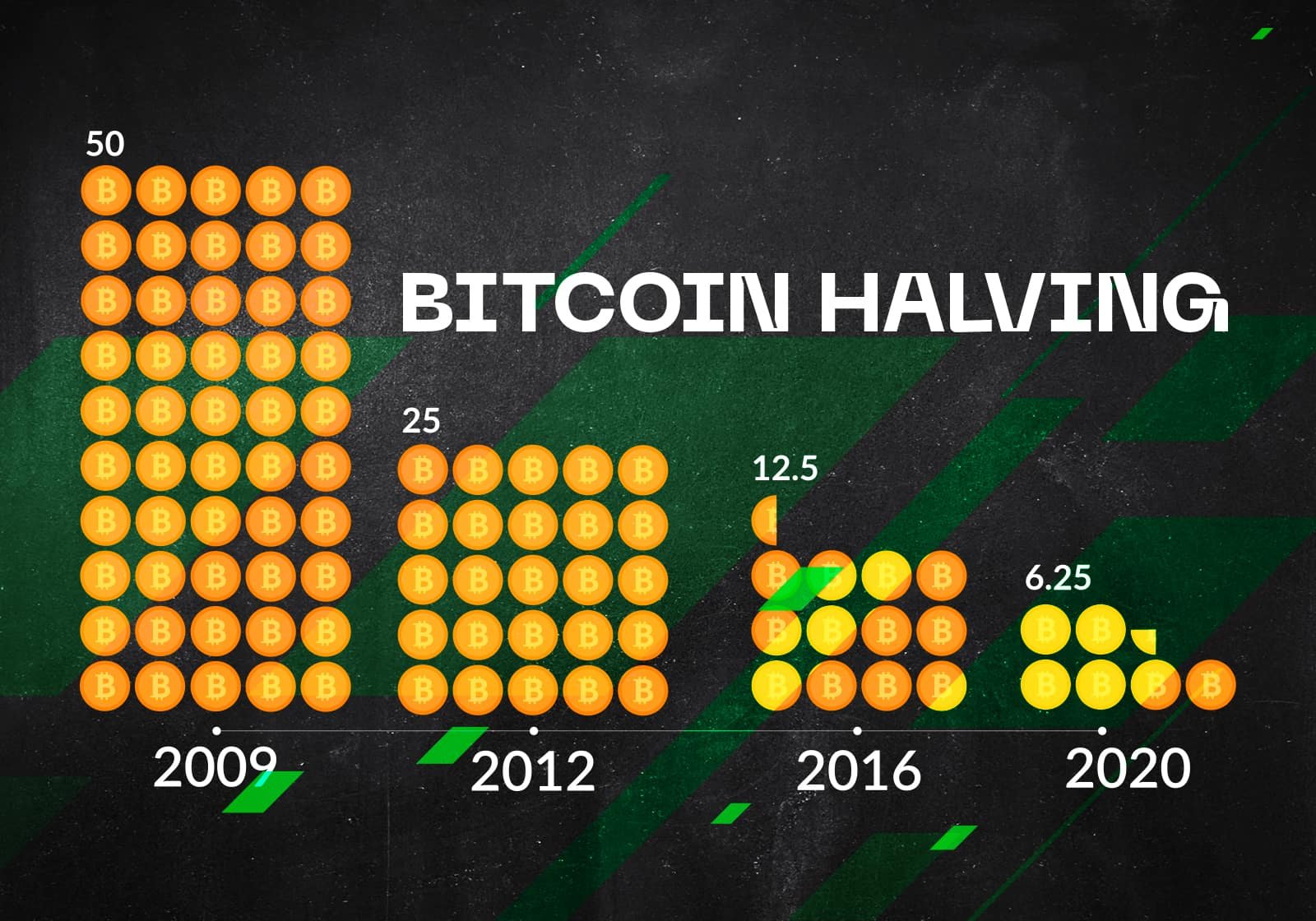
The Bitcoin Halving
Every 210,000 blocks (approx. every 4 years), the amount of Bitcoins that are given as a reward to the miner who solves the block is reduced in half. This event is called the “Bitcoin Halving”. It helps control the supply of bitcoins and ensure that there is a limited amount of them in circulation. Below shows an example of how the Halving works:
Before the halving:
Let’s say that before the halving, the block reward was 12.5 bitcoins per block. So, if a miner was able to solve a block, they would receive 12.5 bitcoins as a reward.
After the halving:
After the halving event, the block reward is reduced by half. So, in this example, the new block reward would be 6.25 bitcoins. This means
that from now on, whenever a miner solves a block, they will only receive 6.25 bitcoins as a reward instead of 12.5.

The halving process helps to control the supply of Bitcoins and ensure that there is a limited amount in circulation. It also ensures that the value of bitcoins remains relatively stable over time. The Halving is the single largest factor as to why we see the Bitcoin price spike upwards in a dramatic fashion every 4 years. That dramatic price increase for each Bitcoin that we see every 4 years helps to balance out the effects of the Halving, allowing the miners to stay profitable even after the rewards are cut in half. The amount of electricity and computing power it takes to mine Bitcoin remains the same even after the rewards are cut in half during the Halving. In order for miners to stay profitable, the price for each of the new Bitcoins mined must increase in order to balance out the reduction in the mining rewards. If the price of each Bitcoin did not increase after each Halving, there would be no incentive for miners to continue to mine and secure the Bitcoin network. This follows the basic fundamentals of supply and demand economics.
Bitcoin Mining is a vital part of the Bitcoin network that helps to keep it secure and running smoothly. By solving complex mathematical problems and adding blocks to the chain, mines are responsible for keeping the network functioning smoothly. The Bitcoin Halving helps play a crucial role in balancing the basic fundamentals of supply and demand by limiting supply and creating value over time through scarcity. Whether you are new to the world of cryptocurrency or simply looking to expand your knowledge, understanding Bitcoin Mining is an important step towards a deeper understanding of how Bitcoin works.

by web3fits | Feb 1, 2023 | Intermediate, Web3Fits
Centralized crypto exchanges, such as FTX, have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way for people to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. However, these centralized exchanges have little to do with the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies themselves. In fact, these exchanges share many similarities with our traditional banking systems today, defeating the premise behind why Bitcoin was created in the first place.
Centralization refers to a system where power and decision-making authority are controlled by a single entity or a small group. Decentralization, on the other hand, refers to a distribution of power and control among multiple entities. Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that was created in response to the 2008 financial crisis, which highlighted the lack of transparency and accountability in our traditional financial system. Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator(s) of Bitcoin, wanted to create a decentralized digital currency that would empower individuals to have more control over their own money and financial transactions. The goal was to create a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that eliminated the need for intermediaries like banks and governments.
One of the key similarities between centralized crypto exchanges and modern-day banking systems is the centralization of power. Just as banks are centralized institutions that control the flow of money, centralized crypto exchanges also control the flow of cryptocurrencies. They act as gatekeepers, determining which cryptocurrencies can be traded and how they can be traded. This goes against the vision of Bitcoin, which is to create a decentralized, transparent system where individuals have more control over their own money and transactions.
Another similarity is the reliance on trust. Just as people trust banks to keep their money safe and to facilitate financial transactions, people also trust centralized crypto exchanges to do the same with their cryptocurrencies. This trust is placed in the hands of a small group of individuals or companies responsible for maintaining the exchange’s infrastructure and ensuring its security. However, this also goes against the idea behind Bitcoin, which is to create a trustless and peer-to-peer system without the need for a third party.
It is very important to understand that centralized authorities can fail. When a bank fails, all the assets you have stored there are in jeopardy of being lost. This has happened numerous times throughout history and highlights the significant control centralized banks hold over our financial assets. Centralized crypto exchanges, such as FTX, also exercise control over users’ assets. The recent collapse of FTX highlights the risks of entrusting funds to a centralized exchange. The same can be said about our current banking system. Technical difficulties or hacks can lead to permanent loss of assets. Hence, before depositing a substantial amount of assets, it’s crucial to assess the level of decentralization and security offered by the exchange.
While centralized crypto exchanges have become an important part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, they have little to do with the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies themselves. They share many similarities with traditional banking systems, and it is important to understand the difference between the two. Ultimately, it is up to the individual to decide whether they want to trust a centralized institution or utilize the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies which is why Bitcoin was created in the first place.










