
by web3fits | Feb 9, 2023 | Beginner, Web3Fits
The history of failed money is a fascinating topic that can teach us important lessons about the value of the currency and the role of government in maintaining a stable economy. Throughout history, there have been countless examples of currencies that have lost value, leading to economic collapses and widespread suffering. Some of the most notable examples include the Roman Empire, Venezuela, Zimbabwe, Ukraine, and Germany.
The root of all these collapses is a lack of faith in the government. When people lose confidence in their government’s ability to maintain a stable economy, they start to hoard currency, causing demand to drop and value to decline. In many cases, this lack of confidence stems from economic mismanagement, corruption, or other factors that undermine the government’s ability to maintain stability.
One of the key causes of currency collapses is inflation. Inflation occurs when the supply of money exceeds demand, leading to an increase in prices. This can happen for a number of reasons, including an increase in the supply of money through printing, a decrease in demand due to hoarding, or a decline in the value of the underlying assets that support the currency. When inflation gets out of control, it can lead to hyperinflation, where prices increase so rapidly that the currency becomes essentially worthless.
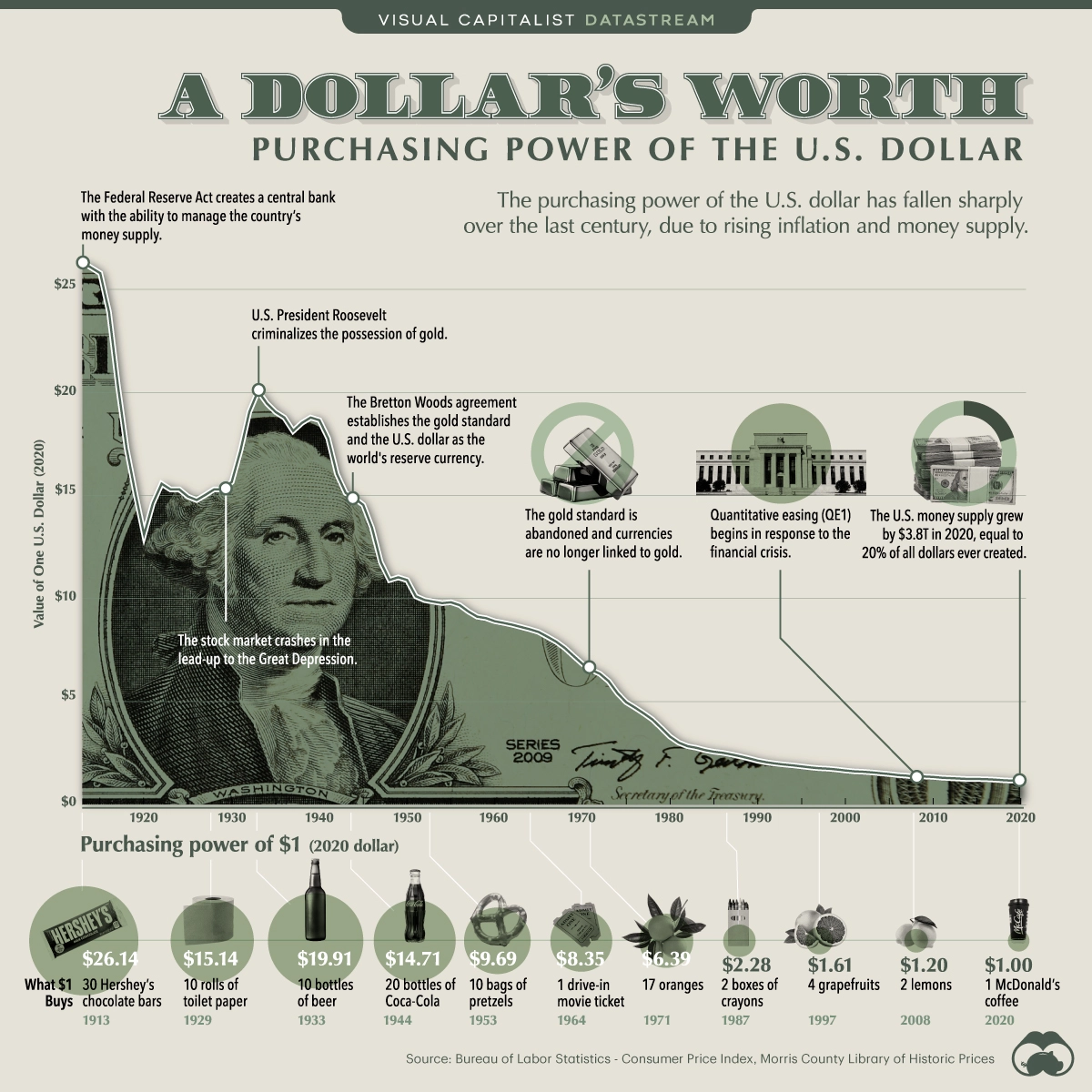
When the government prints more dollars, it adds to the system’s total amount. With more dollars in the system, the value of each dollar decreases. This happened many times in our history, hence why $1 now used to be the value of $26 in 1910.
Cryptocurrency is being viewed as a solution to the problems of inflation and lack of trust in governments. Unlike traditional currencies, which are subject to central control and can be subject to inflationary pressures, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are decentralized and have a limited supply, making them less susceptible to the same issues. Cryptocurrencies use complex algorithms to control their supply, ensuring that inflation remains under control and the currency’s value remains stable.
The creation of cryptocurrency was directly influenced by a lack of faith in government and traditional financial institutions. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the fragility of the global financial system and led to widespread mistrust of banks and governments. This lack of trust led to the creation of Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, as a response to the problems of the traditional financial system. By using cryptography to secure transactions and decentralized networks to record transactions, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer a new way of storing and transferring value that is less susceptible to the issues of inflation and lack of trust that have plagued traditional currencies and financial institutions.
Currency collapses are often the result of a lack of trust in governments and the subsequent inflation that occurs. Cryptocurrency offers a solution to these issues, with its decentralized structure and fixed supply, making it less prone to inflation. The creation of cryptocurrency was a response to the declining trust in traditional financial institutions. By providing a secure, decentralized, and inflation-resistant option for storing and transferring value, cryptocurrency offers a new possibility in the world of finance.

by web3fits | Feb 6, 2023 | Advanced, Web3Fits
Bitcoin is a digital currency that has taken the world by storm. It’s a decentralized form of currency that allows people to make transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Behind the scenes, the process of Bitcoin Mining plays a crucial role in keeping the network secure and functioning properly. In this blog, we will explain what Bitcoin Mining is, how it works, the Bitcoin Halving, why it’s important, and the concept of Proof of Work.
Why is it Called Mining?
Bitcoin mining is called “mining” because it is similar to the process of mining for precious metals or minerals. Just like miners dig deep into the earth to extract gold or other valuable resources, Bitcoin miners use their computer power to “dig” into complex mathematical problems and extract Bitcoins as a reward. The term “mining” was chosen because it accurately describes the process of using computational power to solve problems and extract a reward. It also alludes to the finite nature of the resource, as there is a limited amount of bitcoins that can be mined, just like there is a limited amount of precious minerals that can be extracted from the earth.
Proof of Work
Proof of Work is the process of solving mathematical problems (mining) in order to add a block to the blockchain is called “Proof of Work”. It is a way of ensuring that the blocks are added to the chain in a secure and fair way. Miners have to put in a lot of effort and computing power in order to solve the problems and add the next block to the blockchain.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin Mining is a process where people use computers to solve complex mathematical problems and in return, they get brand new Bitcoins as a reward. Now I know what you thinking, “but Web3Fits, I’m terrible at math!!!”… but don’t worry. The computer handles all the problem-solving while you sit back and enjoy a nice cup of coffee. The process of solving these problems helps to keep the Bitcoin network secure and running smoothly. It is important to note that mining is not the only way to acquire Bitcoins. The process of mining is how brand-new Bitcoins enter the ecosystem. Bitcoins that have already been previously mined can be purchased OTC (over the counter from others Bitcoin holders) or through a cryptocurrency exchange.
How Does Mining Work?
When a problem is solved by a miner, it is called a “block”. Each block contains a list of all the transactions that have taken place on the Bitcoin network since the last block was mined. Miners compete with each other to be the first one to solve the problem and add the next block to the chain. Once a block is added, it cannot be changed, which helps to keep the transaction history secure.
Why is Mining Important?
Mining is important because it helps to keep the Bitcoin network secure and running smoothly. Miners are responsible for adding new blocks to the chain and verifying the transactions that take place on the network. Without mining, the Bitcoin network would not be able to function properly.
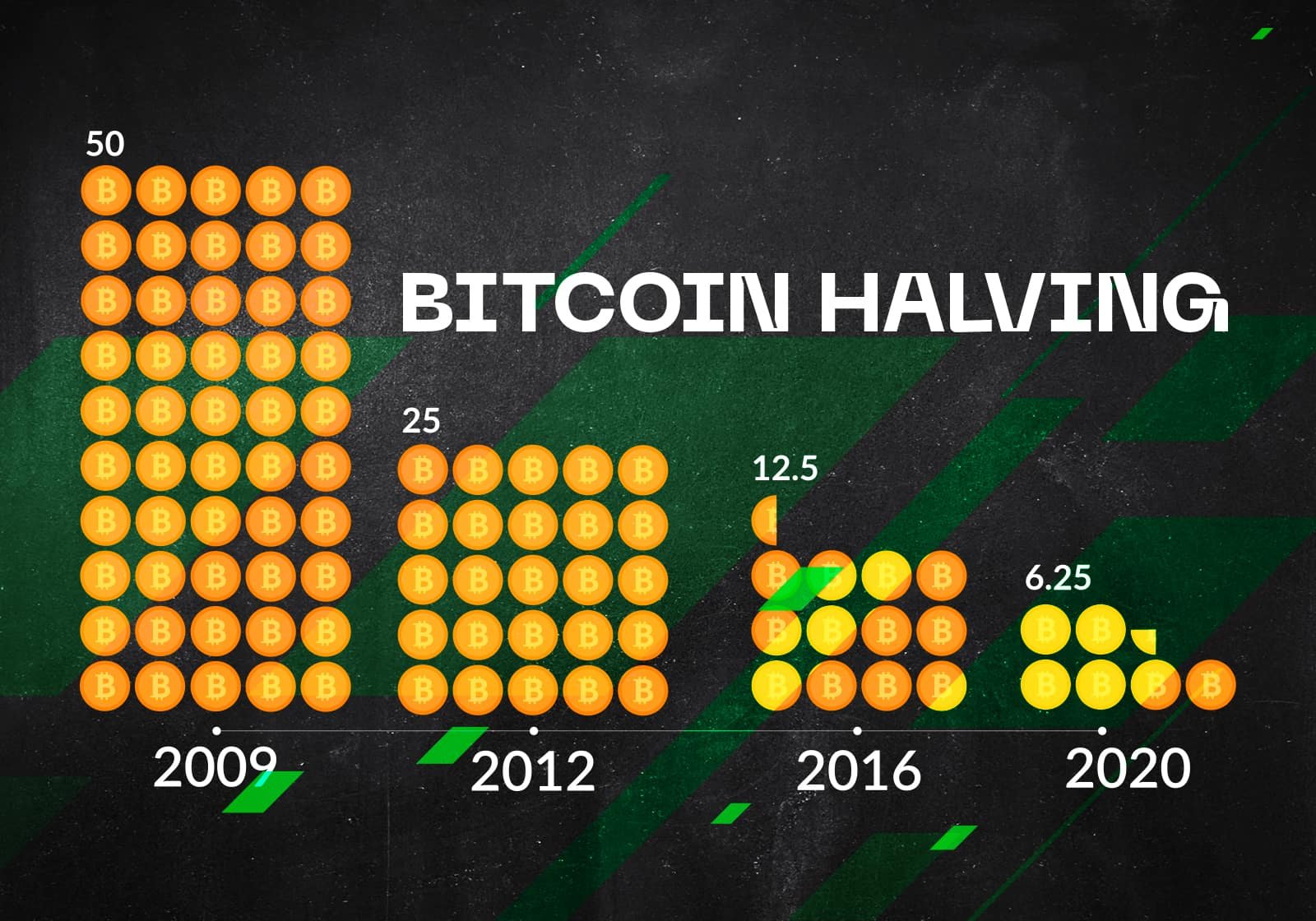
The Bitcoin Halving
Every 210,000 blocks (approx. every 4 years), the amount of Bitcoins that are given as a reward to the miner who solves the block is reduced in half. This event is called the “Bitcoin Halving”. It helps control the supply of bitcoins and ensure that there is a limited amount of them in circulation. Below shows an example of how the Halving works:
Before the halving:
Let’s say that before the halving, the block reward was 12.5 bitcoins per block. So, if a miner was able to solve a block, they would receive 12.5 bitcoins as a reward.
After the halving:
After the halving event, the block reward is reduced by half. So, in this example, the new block reward would be 6.25 bitcoins. This means
that from now on, whenever a miner solves a block, they will only receive 6.25 bitcoins as a reward instead of 12.5.

The halving process helps to control the supply of Bitcoins and ensure that there is a limited amount in circulation. It also ensures that the value of bitcoins remains relatively stable over time. The Halving is the single largest factor as to why we see the Bitcoin price spike upwards in a dramatic fashion every 4 years. That dramatic price increase for each Bitcoin that we see every 4 years helps to balance out the effects of the Halving, allowing the miners to stay profitable even after the rewards are cut in half. The amount of electricity and computing power it takes to mine Bitcoin remains the same even after the rewards are cut in half during the Halving. In order for miners to stay profitable, the price for each of the new Bitcoins mined must increase in order to balance out the reduction in the mining rewards. If the price of each Bitcoin did not increase after each Halving, there would be no incentive for miners to continue to mine and secure the Bitcoin network. This follows the basic fundamentals of supply and demand economics.
Bitcoin Mining is a vital part of the Bitcoin network that helps to keep it secure and running smoothly. By solving complex mathematical problems and adding blocks to the chain, mines are responsible for keeping the network functioning smoothly. The Bitcoin Halving helps play a crucial role in balancing the basic fundamentals of supply and demand by limiting supply and creating value over time through scarcity. Whether you are new to the world of cryptocurrency or simply looking to expand your knowledge, understanding Bitcoin Mining is an important step towards a deeper understanding of how Bitcoin works.

by web3fits | Feb 1, 2023 | Intermediate, Web3Fits
Centralized crypto exchanges, such as FTX, have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way for people to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. However, these centralized exchanges have little to do with the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies themselves. In fact, these exchanges share many similarities with our traditional banking systems today, defeating the premise behind why Bitcoin was created in the first place.
Centralization refers to a system where power and decision-making authority are controlled by a single entity or a small group. Decentralization, on the other hand, refers to a distribution of power and control among multiple entities. Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that was created in response to the 2008 financial crisis, which highlighted the lack of transparency and accountability in our traditional financial system. Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator(s) of Bitcoin, wanted to create a decentralized digital currency that would empower individuals to have more control over their own money and financial transactions. The goal was to create a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that eliminated the need for intermediaries like banks and governments.
One of the key similarities between centralized crypto exchanges and modern-day banking systems is the centralization of power. Just as banks are centralized institutions that control the flow of money, centralized crypto exchanges also control the flow of cryptocurrencies. They act as gatekeepers, determining which cryptocurrencies can be traded and how they can be traded. This goes against the vision of Bitcoin, which is to create a decentralized, transparent system where individuals have more control over their own money and transactions.
Another similarity is the reliance on trust. Just as people trust banks to keep their money safe and to facilitate financial transactions, people also trust centralized crypto exchanges to do the same with their cryptocurrencies. This trust is placed in the hands of a small group of individuals or companies responsible for maintaining the exchange’s infrastructure and ensuring its security. However, this also goes against the idea behind Bitcoin, which is to create a trustless and peer-to-peer system without the need for a third party.
It is very important to understand that centralized authorities can fail. When a bank fails, all the assets you have stored there are in jeopardy of being lost. This has happened numerous times throughout history and highlights the significant control centralized banks hold over our financial assets. Centralized crypto exchanges, such as FTX, also exercise control over users’ assets. The recent collapse of FTX highlights the risks of entrusting funds to a centralized exchange. The same can be said about our current banking system. Technical difficulties or hacks can lead to permanent loss of assets. Hence, before depositing a substantial amount of assets, it’s crucial to assess the level of decentralization and security offered by the exchange.
While centralized crypto exchanges have become an important part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, they have little to do with the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies themselves. They share many similarities with traditional banking systems, and it is important to understand the difference between the two. Ultimately, it is up to the individual to decide whether they want to trust a centralized institution or utilize the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies which is why Bitcoin was created in the first place.

by web3fits | Jan 5, 2023 | Beginner, Web3Fits
What is money? Many of us think we know the answer to that question, but few truly understand what money is and what gives it value. The history of money is a fascinating one that has evolved significantly over time. From the barter system to precious metals, to paper money, to cryptocurrencies, the way we exchange goods and services has undergone significant changes throughout human history. In order to understand the future of our money, we must first take a trip down memory lane.
The Barter System
Before the concept of money, people relied on the barter system to exchange goods and services. This involved trading one good or service for another, without using a common currency. For example, someone might trade a chicken for a basket of apples.
While the barter system was effective in some cases, it had its limitations. It was challenging to find someone who wanted the exact good or service you had to offer, and it was impossible to easily compare the value of different goods and services.

The Transition to Precious Metals
To address these limitations, people began to use precious metals, such as gold and silver, as a form of currency. Precious metals were widely accepted, as they had a universal value and could be easily stored and transported.
The use of precious metals as a form of currency led to the creation of minted coins, which could be easily traded and recognized as a specific value. This made it easier to compare the value of different goods and services and facilitated trade between different cultures and civilizations.
The Transition to Paper Money
As societies became more complex and trade increased, the use of precious metals as a form of currency became impractical. It was difficult to transport and store large quantities of gold and silver, and the production of minted coins was time-consuming and costly.
To address these issues, governments began to issue paper money that was backed by gold or other precious metals. This allowed for the easy exchange of currency, and people could hold paper money as a representation of their wealth.

The USA Going Off the Gold Standard
In the 20th century, the United States abandoned the gold standard and began to issue fiat money, which is not backed by a commodity. This allowed the government to print more money as needed, which helped stimulate economic growth and provided a convenient way to exchange goods and services.
However, the downside of fiat money is that it is not backed by a tangible asset, and its value is based on the trust and confidence of the issuing government. This can lead to inflation and devaluation of the currency, as the government can print more money than there is gold or other assets to back it up.
The Creation of Cryptocurrencies
In recent years, the emergence of cryptocurrencies has offered a new way to exchange goods and services without the need for a central authority. Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, are decentralized digital currencies that use blockchain technology to record transactions and verify ownership.
One of the main advantages of cryptocurrencies is that they are not subject to the same central control and manipulation as fiat currencies. They are also backed by a decentralized network of computers, rather than a single government or institution.
While cryptocurrencies are still in the early stages of adoption, they have the potential to revolutionize the way we exchange goods and services and offer a more secure and transparent alternative to the current fiat system.
The history of money is a complex and fascinating one that has evolved significantly over time. From the barter system to precious metals, to paper money, and now cryptocurrencies, the way we exchange goods and services has undergone significant changes throughout human history. While the current fiat system has its advantages, the emergence of cryptocurrencies offers the potential for a more secure and transparent way to exchange goods and services in the future.

by web3fits | Jan 3, 2023 | Advanced, Web3Fits
Cryptography has a long history that dates back to ancient civilizations. It is believed to have been created as a way for people to communicate secret messages to each other without others being able to understand the information.
The origins of cryptography can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. These civilizations used simple codes and ciphers to communicate with each other and protect their information from enemies. For example, the Egyptians used hieroglyphics to write secret messages, while the Greeks and Romans used simple substitution ciphers to encode their messages.
As societies became more complex and communication technologies improved, cryptography also evolved. During World War II, both the Allies and the Axis powers made extensive use of cryptography to protect their communications and gain an advantage over their enemies.

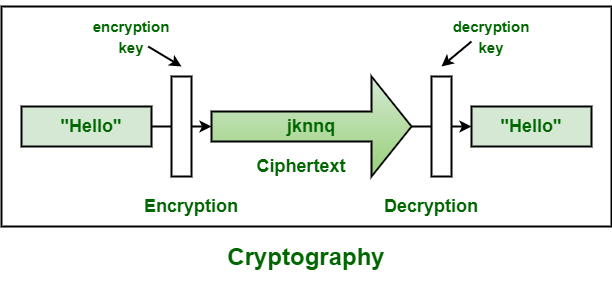
Nowadays, cryptography is used in online banking to protect your financial information and keep it safe from hackers. When you enter your login information or make a purchase online, the information is encrypted (or turned into a code) so that no one can see what you’re doing. This way, you can feel confident that your money and personal information are safe.
Cryptography is also used to create passwords for your online accounts. When you create a password, it is encrypted and stored in a special way that makes it hard for anyone to guess. This way, only you will be able to access your accounts.
In the world of cryptocurrencies, cryptography helps to keep all users within the network safe. Cryptocurrency is a type of digital money that uses cryptography to secure transactions and prevent fraud. Cryptocurrency works by using a special code called a “blockchain” to keep track of all the transactions that have been made. Each transaction is encrypted and added to the blockchain, making it very hard for anyone to change or alter the information. Cryptography helps to ensure that the system is secure and trustworthy. Without cryptography, it would be much easier for people to cheat or steal from the system, which could cause problems for everyone who uses it.














