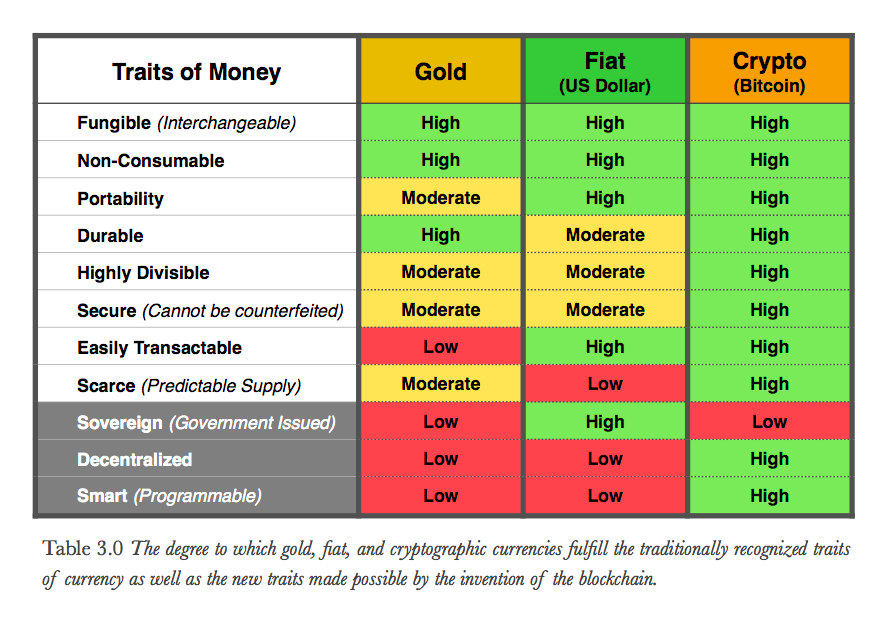
The history of failed money is a fascinating topic that can teach us important lessons about the value of the currency and the role of government in maintaining a stable economy. Throughout history, there have been countless examples of currencies that have lost value, leading to economic collapses and widespread suffering. Some of the most notable examples include the Roman Empire, Venezuela, Zimbabwe, Ukraine, and Germany.
The root of all these collapses is a lack of faith in the government. When people lose confidence in their government’s ability to maintain a stable economy, they start to hoard currency, causing demand to drop and value to decline. In many cases, this lack of confidence stems from economic mismanagement, corruption, or other factors that undermine the government’s ability to maintain stability.
One of the key causes of currency collapses is inflation. Inflation occurs when the supply of money exceeds demand, leading to an increase in prices. This can happen for a number of reasons, including an increase in the supply of money through printing, a decrease in demand due to hoarding, or a decline in the value of the underlying assets that support the currency. When inflation gets out of control, it can lead to hyperinflation, where prices increase so rapidly that the currency becomes essentially worthless.
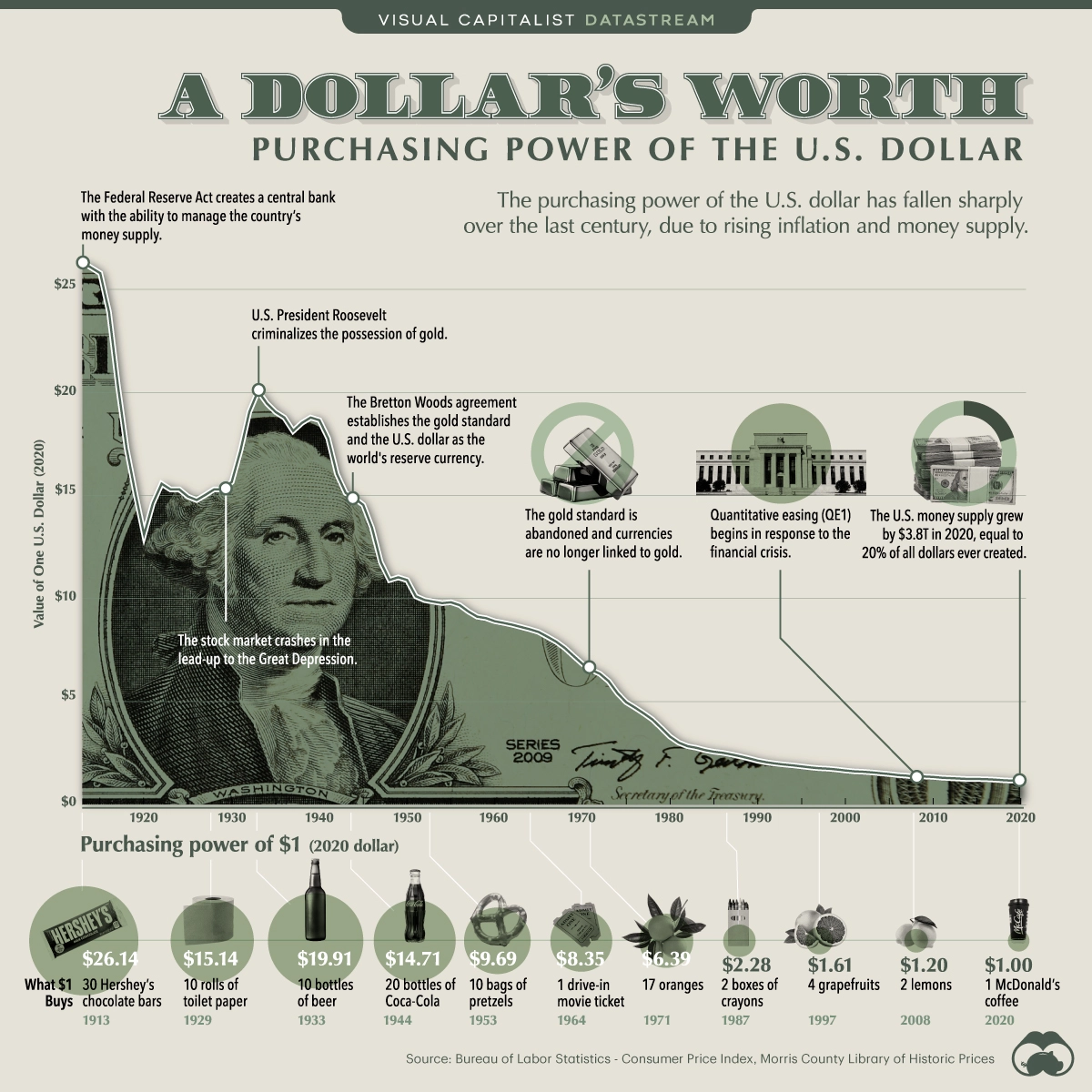
When the government prints more dollars, it adds to the system’s total amount. With more dollars in the system, the value of each dollar decreases. This happened many times in our history, hence why $1 now used to be the value of $26 in 1910.
Cryptocurrency is being viewed as a solution to the problems of inflation and lack of trust in governments. Unlike traditional currencies, which are subject to central control and can be subject to inflationary pressures, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are decentralized and have a limited supply, making them less susceptible to the same issues. Cryptocurrencies use complex algorithms to control their supply, ensuring that inflation remains under control and the currency’s value remains stable.
The creation of cryptocurrency was directly influenced by a lack of faith in government and traditional financial institutions. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the fragility of the global financial system and led to widespread mistrust of banks and governments. This lack of trust led to the creation of Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, as a response to the problems of the traditional financial system. By using cryptography to secure transactions and decentralized networks to record transactions, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer a new way of storing and transferring value that is less susceptible to the issues of inflation and lack of trust that have plagued traditional currencies and financial institutions.
Currency collapses are often the result of a lack of trust in governments and the subsequent inflation that occurs. Cryptocurrency offers a solution to these issues, with its decentralized structure and fixed supply, making it less prone to inflation. The creation of cryptocurrency was a response to the declining trust in traditional financial institutions. By providing a secure, decentralized, and inflation-resistant option for storing and transferring value, cryptocurrency offers a new possibility in the world of finance.