Blockchain technology is the backbone of cryptocurrency. It was originally developed as the underlying infrastructure for cryptocurrency transactions. However, the potential applications of blockchain technology go far beyond cryptocurrency. One of the key benefits of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Because there is no central authority controlling the blockchain, it is much more difficult for fraud or corruption to take place. In addition, blockchain transactions are immutable, meaning that they cannot be altered or deleted once they have been recorded. This makes blockchain an ideal platform for conducting financial transactions, as well as other types of sensitive information.
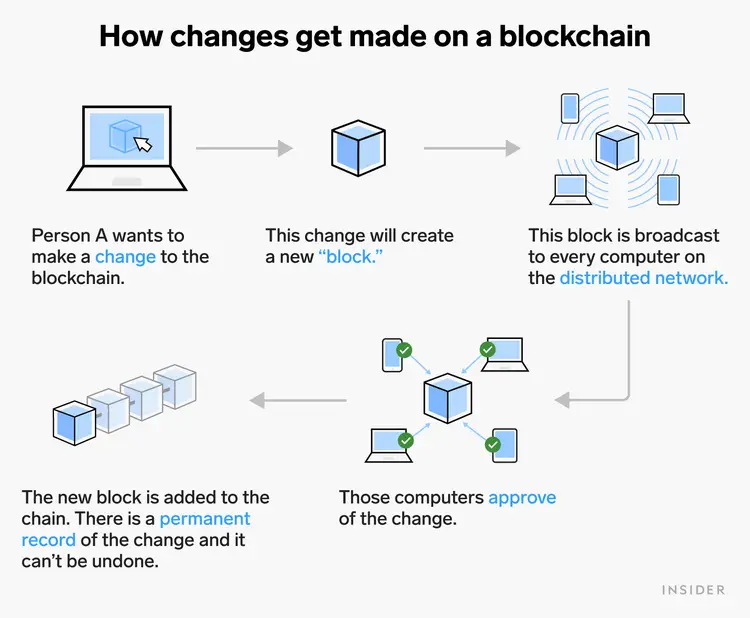
Another benefit of blockchain is that it is highly secure. The combination of decentralization and immutability makes it very difficult for hackers to tamper with data on the blockchain. So what is it and how does it work? For starters, IBM defines Blockchain as: “a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a network. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.” In simple terms: Blockchain is a “digital book” that records, stores, and shares information in real-time. Each time a transaction is made on the network, the transaction is recorded on a “block” which is then added to a “chain” of existing blocks. Hence, the term “blockchain”. Each one of these blocks acts as a new page in the “digital book.”
When was it first created?
The blockchain network was created during the development of Bitcoin in 2008 as a way to record all transactions made on the network without the need for a third party like a bank.
Why is it important?
Since blockchain technology lives on the internet, transactions can be made 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Information is sent/received quickly and accurately and is permanently stored on a highly secure network, all without the need for a controlling party. Blockchain technology offers today’s cheapest, fastest, and most secure database.
 As we mentioned earlier, the potential applications of blockchain technology go far beyond cryptocurrency. The combination of decentralization and immutability makes it very difficult for hackers to tamper with data on the blockchain. As a result, many institutions are beginning to explore the use of blockchain technology for a variety of applications. Let’s explore how some of these institutions are using blockchain today:
As we mentioned earlier, the potential applications of blockchain technology go far beyond cryptocurrency. The combination of decentralization and immutability makes it very difficult for hackers to tamper with data on the blockchain. As a result, many institutions are beginning to explore the use of blockchain technology for a variety of applications. Let’s explore how some of these institutions are using blockchain today:
IBM Blockchain -Knowing the status and condition of every product in the supply chain from raw materials to distribution. -Blockchain helps supply chains keep a record of parts and products in real-time.
Food Industry -Improve the efficiency of tracing sources of contaminated foods. -Deter false claims of ingredients and sources of food products.
Diamond Mining -The De Beers Group, which mines 30% of the world’s supply of diamonds, plans to use a blockchain to trace diamonds from the mine to the customer. -Transparency in verifying diamond authenticity and ensuring they were mined free from conflict. These are just small samples of real-world use cases for blockchain technology. Many other industries such as healthcare, retail, automobile, real estate, and more are beginning to experiment with using blockchain technology to better their industries. By providing a secure, transparent way to conduct transactions, blockchain not only has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry but every industry around the world.
